This new study, led by experts from the Chinese Academy of Sciences and published in the journal Personality and Individual Differences, even digs into some possible reasons why this particular body shape holds so much appeal.

The Study Methodology
To conduct their research, the scientists recruited a group of 283 people from three countries: China, Lithuania, and the United Kingdom.
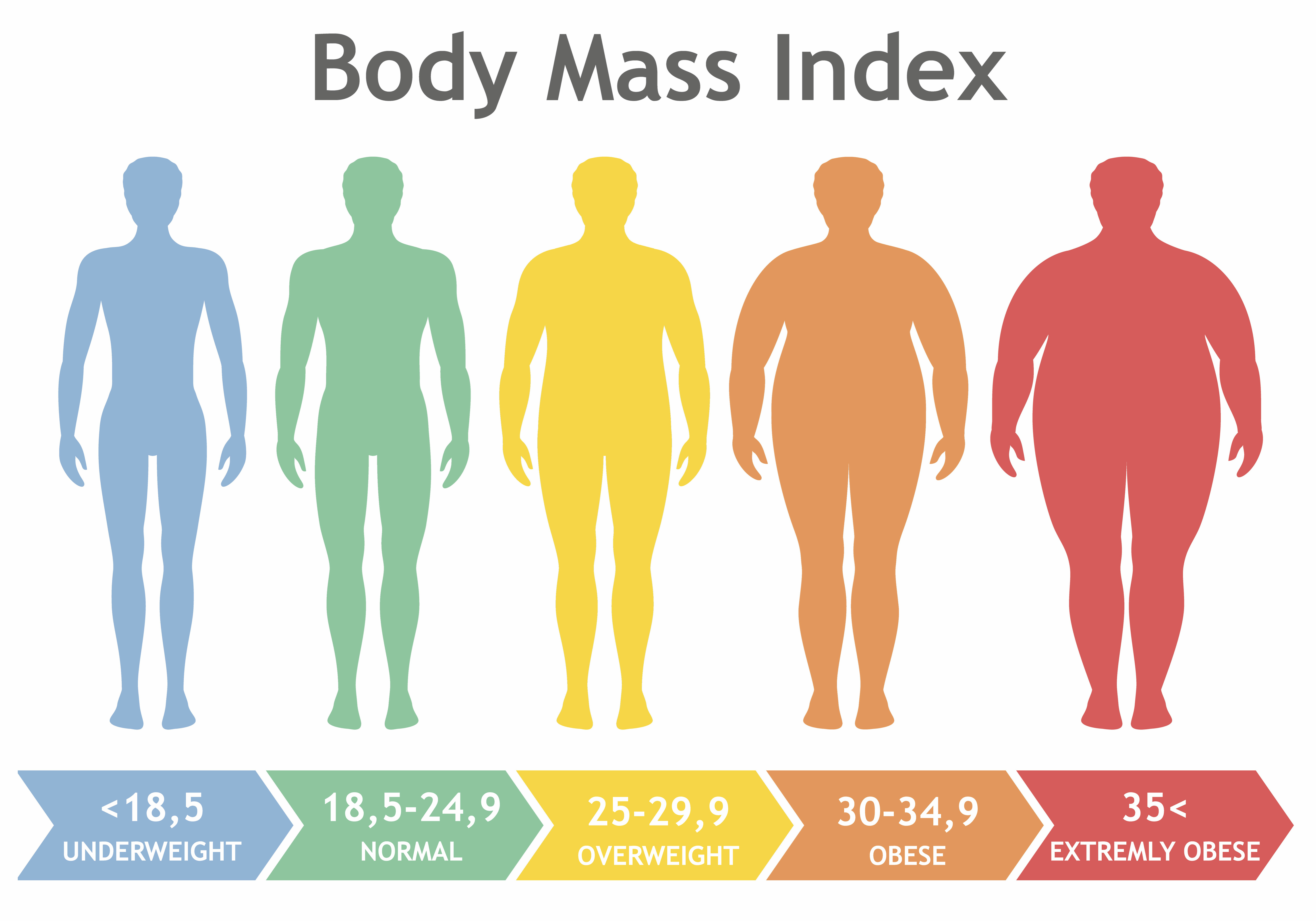
Each participant was shown a series of 15 black-and-white images of men, each representing different body mass index (BMI) levels.
The researchers blurred out the faces in the images so participants could focus only on body shape.
Then, they were asked to rank the bodies from least attractive to most attractive.
The data revealed that the most desirable male bodies had a BMI between 23 and 27.
In Lithuania, 23.0 was considered the most appealing. And in the UK, the sweet spot was a little higher at 26.6.
So, what the results tell us is that it’s not the ultra-slim or gym-chiseled bodies that rank highest in attractiveness, but rather those with a bit more substance.
What This Means
While the visual preferences were interesting on their own, what really caught the researchers’ attention was the reason behind them.
“Body fat (adiposity) may be important because it is linked closely (inversely) to circulating testosterone levels and is therefore a better indicator of mate ‘quality’,” the researchers explained.
Essentially, having a medium-range BMI may signal that someone is both healthy and well-suited for survival and reproduction, which plays into evolutionary preferences.

However, the story changes a bit when it comes to female body types.
Earlier research from the same team showed that when men judge women’s attractiveness, they tend to find body types thinner than the “evolutionary optimal” more appealing.
